Water Safety for Dogs: Swimming Pool and Beach Precautions
Understanding Coastal Hazards
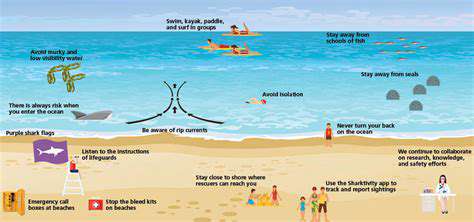
Coastal environments present unique challenges despite their beauty. Recognizing potential dangers forms the foundation of safe beach outings. Hazards include powerful currents, unpredictable riptides, sudden depth changes, and rapidly shifting weather conditions. Developing awareness and response strategies for these situations is essential.
Rip currents demand particular attention - these fast-moving water channels can overpower even strong swimmers. They typically form near drop-offs or sandbars, appearing as narrow, turbulent water paths flowing seaward. Learning to identify these dangerous currents significantly enhances safety in ocean environments.
Essential Beach Safety Gear
Proper equipment selection dramatically improves beach safety. A personal flotation device (PFD) offers critical security, even for confident swimmers venturing beyond comfort zones. In emergencies, these devices can prove lifesaving.
Sun protection remains equally vital. High-quality sunscreen, protective hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses prevent sun damage to skin and eyes during extended exposure.
Recognizing Rip Currents
Spotting rip currents requires practiced observation. Look for unusual water patterns - typically choppy, discolored channels running perpendicular to shore. These visual indicators often signal dangerous currents beneath the surface.
Observe fellow beachgoers carefully, as those caught in currents provide visible warnings. Never attempt unassisted rescues; instead, immediately alert trained lifeguards or emergency services.
Respecting Water Depth
Depth awareness prevents many beach accidents. Gradual slopes can suddenly drop off, creating hazardous conditions. Always test water depth before full entry, especially in unfamiliar locations. Simple probing with feet or a stick helps identify potential dangers.
Remain vigilant for submerged obstacles like rocks or coral formations that could cause injury upon contact.
Weather Awareness
Coastal weather changes rapidly, significantly impacting safety conditions. Consistent monitoring of weather forecasts and warnings should precede all beach visits. Sudden storms, strong winds, or rapidly rising tides create dangerous situations for unprepared visitors.
Develop awareness of approaching storms and lightning activity. Always maintain accessible exit routes from the beach when weather threatens.
First Aid and Emergency Procedures
Basic first aid knowledge proves invaluable during emergencies. Learn proper treatment for common beach injuries like cuts or abrasions. CPR training significantly improves survival chances during cardiac or respiratory emergencies.
Note lifeguard station locations and local emergency contact information before entering the water. Quick access to professional help can save lives.
Staying Informed About Beach Conditions
Current condition awareness forms the cornerstone of beach safety. Regularly check updated weather reports, tide charts, and official warnings. This information enables informed decisions about water activities and appropriate safety measures.
Updated resources provide critical insights into changing conditions, allowing for proper activity planning and risk assessment.

Protecting Paws and Preventing Accidents
Doggy Water Safety: Understanding the Risks
Dogs naturally gravitate toward water during warm weather, but this attraction carries inherent risks requiring careful management. Owners must develop keen awareness of potential dangers in all aquatic environments - from swimming pools to natural bodies of water. Proactive safety measures become essential for protecting our four-legged friends.
Even apparently strong swimmers can encounter difficulties when facing unexpected water conditions. Sudden depth changes, hidden obstacles, or strong currents can quickly transform recreation into emergency situations. Risk awareness forms the first line of defense against water-related accidents.
Pool Safety Protocols
Residential pools present particular dangers without proper precautions. Secure perimeter fencing provides essential containment, though constant supervision remains critical regardless of physical barriers. Never compromise on direct observation, even momentarily.
Supplementary safety measures like pool covers or floating alarms offer additional protection when pools aren't in active use. These precautions provide peace of mind while significantly reducing accident risks.
Recognizing Warning Signs
Canine distress signals often appear subtle to untrained observers. Excessive paddling, disorientation, or unusual vocalizations indicate potential trouble. Immediate intervention becomes crucial when noticing any abnormal behaviors.
Learn to identify early fatigue signs like slowed movements or decreased responsiveness. Prompt removal from water and rest periods prevent more serious complications.
Water-Specific Dangers for Dogs
Beyond obvious drowning risks, water presents several less apparent hazards. Chemical exposure from treated pools can irritate skin and mucous membranes. Natural water sources may contain harmful microorganisms or toxins. Water temperature extremes also pose significant risks, potentially causing shock or hypothermia.
Emergency Preparedness
Develop and practice water emergency response plans. Learn proper techniques for assisting distressed dogs without endangering yourself. Preparation and knowledge dramatically improve outcomes during critical situations.
Training and Prevention
Early, positive water introductions build confidence and safety awareness. Use reward-based methods to create positive associations with aquatic environments. Consistent reinforcement of safety boundaries establishes lifelong safe habits.
Gradual exposure under controlled conditions helps dogs develop necessary skills while allowing owners to monitor comfort levels and abilities.
Essential Gear and Preparation for Safe Water Fun
Essential Safety Gear for Canine Swimmers
Proper equipment selection forms the foundation of aquatic safety. A well-fitted canine life vest provides critical buoyancy, reducing fatigue and panic risks. Choose models specifically designed for swimming activities, ensuring proper fit without restricting movement. Quality construction and proper sizing make these devices truly effective.
Specialized water leashes offer control without entanglement risks. Opt for buoyant, quick-release designs that maintain safety while allowing freedom of movement. These specialized tools prove far superior to standard leashes in aquatic environments.
Understanding Your Dog's Swimming Abilities
Recognize that swimming ability varies significantly among individual dogs. Observe natural reactions to water - some demonstrate immediate comfort while others show hesitation or fear. Respect these individual differences and never force participation.
Begin with brief, positive experiences in shallow water, gradually increasing duration and depth as confidence grows. Continuous observation of body language ensures activities remain within comfort zones.
Prioritizing Water Conditions and Supervision
Thoroughly assess aquatic environments before allowing access. Avoid areas with strong currents, poor visibility, or hazardous debris. Constant supervision remains essential, regardless of location or perceived safety.
Preparing for Emergencies and First Aid
Maintain a canine-specific first aid kit containing essential supplies for water-related injuries. Include waterproof bandages, antiseptic solutions, and emergency contact information. Familiarity with basic procedures enables effective response to common issues.
Choosing the Right Location and Time
Select aquatic environments carefully, considering factors like water quality, accessibility, and potential hazards. Avoid peak heat hours to prevent overheating. Environmental awareness significantly enhances safety for water-loving dogs.
Read more about Water Safety for Dogs: Swimming Pool and Beach Precautions
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet