Recognizing Signs of Dehydration in Winter
Other telltale signs include muscle cramps (especially in legs), decreased urination, dark yellow urine, or constant dry mouth. Recognizing these early warnings helps prevent more serious complications from prolonged dehydration in cold weather.
Chronic dehydration can trigger additional health issues like digestive problems or recurring headaches. Staying alert to these subtle signs proves crucial for maintaining winter wellness. Early detection allows for timely intervention, preventing more severe health consequences.
How Indoor Heating and Cold Air Affect Hydration
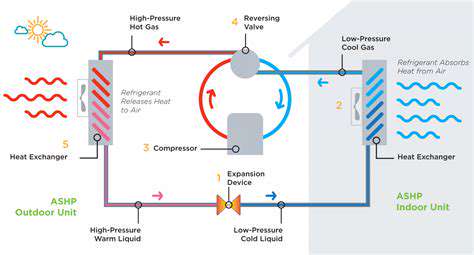
Energy Demands of Indoor Heating
Heating systems, whether conventional furnaces or modern heat pumps, consume substantial energy. This consumption directly ties to fossil fuel use and carbon emissions. Understanding different heating methods' energy footprints helps make informed choices about efficiency and sustainability.
Upgrading to energy-efficient systems can dramatically cut consumption compared to older models. Pairing these with smart thermostats and regular maintenance yields long-term savings on energy bills while reducing environmental impact.
Indoor Air Quality Health Effects
While providing warmth, heating systems often degrade indoor air quality. The resulting dry air can aggravate respiratory conditions like asthma. Strategic use of humidifiers and proper ventilation helps counteract these negative effects, improving home health environments.
Economic Realities of Heating Costs
Heating expenses consume significant portions of household budgets during cold months, with energy price fluctuations adding financial stress. Adopting energy-efficient practices and making smart heating choices can meaningfully reduce this economic burden.
Regions with harsh winters particularly feel this strain, where high energy consumption directly translates to steep utility bills affecting overall living affordability.
Environmental Consequences of Heating
Fossil fuel-based heating systems contribute substantially to greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar thermal systems or electric heat pumps powered by clean energy is essential for reducing this environmental impact.
Innovations in Heating Technology
Technological advances continuously improve heating efficiency and sustainability. Smart thermostats, advanced insulation, and heat pump innovations are making heating more eco-friendly while enhancing comfort and affordability.
The future points toward greater smart home integration, enabling personalized heating approaches that minimize energy waste while optimizing user experience.
Nutritional Adjustments for Winter Hydration

Winter's Impact on Dietary Requirements
Cold weather alters nutritional needs as shorter days and lower temperatures affect energy demands. Adapting diets to include immune-boosting vitamin C and sustained-energy complex carbohydrates becomes particularly important during winter months.
Some experience decreased appetite in winter, but this shouldn't mean neglecting nutrition. Hearty, nutrient-dense meals like soups and roasted vegetables provide both warmth and essential nourishment. Meal planning with varied, nutrient-rich options helps maintain balanced winter nutrition.
Cold-Weather Nutrition Strategies
Winter demands foods that support warmth and energy. Healthy fats from avocados and nuts help regulate body temperature - especially valuable during cold months. Lean proteins from chicken or fish support muscle function and overall vitality when managing winter energy levels.
Seasonal produce like root vegetables delivers essential vitamins and minerals while adding flavor to winter meals. Carrots, sweet potatoes, and parsnips work well in various dishes, ensuring nutritional balance during colder seasons.
Sustaining Energy and Immunity
With typically reduced winter activity, maintaining energy requires focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains and legumes. Adequate protein intake also helps preserve muscle mass and energy reserves.
Supporting immune function becomes critical during winter. Antioxidant-rich foods like berries and citrus fruits help combat seasonal illnesses while protecting cells from damage. These natural defenses prove invaluable against winter viruses.
Practical Winter Hydration Strategies

Understanding Hydration Needs
Proper hydration underpins numerous bodily functions from temperature regulation to nutrient transport. Individual needs vary based on activity levels, climate, and health factors - making personalized awareness crucial.
While eight daily glasses serves as general guidance, thirst signals provide more accurate indicators. Ignoring these cues risks dehydration, potentially leading to fatigue and headaches.
Effective Hydration Methods
Beyond water, flavorful alternatives like fruit-infused waters or herbal teas boost intake without added sugars. Electrolyte drinks help replenish minerals after exertion, though unsweetened varieties are preferable.
Keeping a reusable water bottle handy serves as both reminder and convenience for consistent hydration throughout the day. This simple habit significantly improves daily fluid intake.
Exercise Hydration Essentials
Physical activity increases fluid loss dramatically. Strategic hydration before, during, and after workouts maintains performance and prevents dehydration. Regular small sips prove more effective than occasional large quantities.
Recognizing dehydration signs during exercise allows for timely adjustments. For extended sessions, consider electrolyte-replenishing sports drinks to complement water intake.
Diet's Role in Hydration
Many foods contribute significantly to fluid intake. Water-rich fruits and vegetables like watermelon, cucumbers, and leafy greens boost hydration without extra drinking. Soups and broths offer nutrient-dense hydration options.
Moderating dehydrating substances like caffeine and alcohol helps maintain fluid balance. Awareness of dietary impacts on hydration creates more comprehensive wellness strategies.
Special Hydration Considerations
Certain health conditions require tailored hydration approaches. Those with kidney issues or taking specific medications should consult healthcare providers for personalized fluid intake recommendations.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding increase fluid needs substantially. Medical guidance ensures proper hydration supports these critical physiological states. Professional advice proves invaluable for unique health circumstances.