Urinalysis for Pets: What It Can Tell You
Understanding the Significance of Urine Analysis
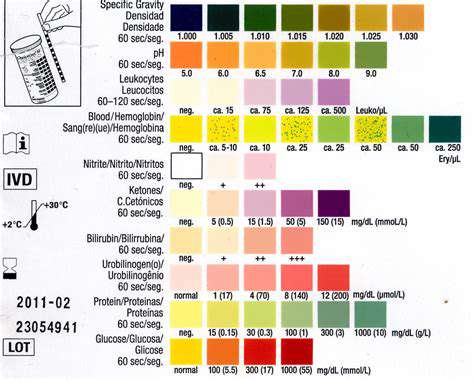
Urine analysis, a fundamental diagnostic tool in healthcare, provides valuable insights into the overall health and well-being of an individual. It is a simple, non-invasive procedure that can detect a wide range of conditions, from mild infections to serious kidney diseases. The examination of urine components reveals crucial information about the body's metabolic processes and the functioning of various organs, especially the kidneys. This analysis involves a careful evaluation of the physical characteristics, chemical composition, and microscopic examination of the urine sample.
By analyzing the color, clarity, and specific gravity of the urine, healthcare professionals can often identify potential imbalances in the body's fluid balance. Variations in these characteristics can hint at dehydration, urinary tract infections, or other underlying conditions. The presence of abnormal substances like glucose, protein, or blood cells in the urine can also serve as important indicators of various health issues. A detailed examination of these components can lead to early diagnosis and prompt treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Interpreting Urine Components for Diagnostic Purposes
The chemical composition of urine, including the presence of various electrolytes, glucose, proteins, and other substances, offers a wealth of information about the body's metabolic state. For example, the presence of excessive glucose in the urine (glycosuria) can be a strong indicator of diabetes, while the presence of protein (proteinuria) might suggest kidney damage or other underlying conditions. These findings often trigger further investigation and specialized tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Microscopic examination of the urine sediment is another crucial aspect of analysis. The presence of abnormal cells, casts, or crystals can provide valuable clues about the health of the urinary system and other organs. For example, the presence of red blood cells in the urine (hematuria) could indicate a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or even more serious conditions, such as cancer. Careful analysis of these microscopic elements is critical in pinpointing the source of the problem.
Furthermore, the analysis of urine components can aid in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments. By tracking changes in the urine's composition over time, healthcare professionals can assess whether a particular treatment plan is yielding the desired results. This ongoing monitoring is particularly important in managing chronic conditions and ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care. Regular urine analysis can serve as an important early warning system for potential health issues.
Common Reasons for Performing a Pet Urinalysis

Common Reasons for Performing a PET Scan
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan is a specialized imaging technique that provides valuable insights into the metabolic activity of tissues within the body. This metabolic activity can often reveal the presence of disease processes, allowing for earlier detection and more effective treatment. Understanding the various reasons why a PET scan might be ordered is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike. The scan can detect abnormalities in metabolic activity that may not be visible on other imaging techniques like X-rays or CT scans.
One primary reason for ordering a PET scan is to evaluate suspected cancers. By identifying areas of increased metabolic activity, doctors can potentially detect the presence of tumor growth or metastasis. This early detection can significantly impact treatment outcomes and improve patient prognosis. The scan can also help determine the extent of the disease, aiding in the planning of surgical procedures or radiation therapy.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Treatment
PET scans can be instrumental in monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. By comparing metabolic activity before and after treatment, doctors can assess whether the treatment is successfully targeting and reducing the tumor burden. This ongoing evaluation helps refine treatment plans and optimize outcomes.
The ability to detect changes in metabolic activity is crucial in determining the success of treatment. By tracking these changes over time, doctors can make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring that it is providing the best possible outcomes for the patient. A PET scan can provide a dynamic picture of the treatment process, allowing for timely interventions and better patient management.
Furthermore, PET scans can be used to evaluate the overall response of the body to treatment. This can reveal how the patient's body is reacting to the treatment plan and allow for adjustments to be made as needed. This broader assessment is critical to optimizing treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects. This is particularly important for patients undergoing aggressive treatment regimens.
Diagnosing Other Medical Conditions
While most commonly associated with cancer diagnosis and treatment monitoring, PET scans can also aid in the diagnosis of various other medical conditions. Conditions such as neurological disorders, infections, and inflammatory diseases can manifest as changes in metabolic activity that are detectable via a PET scan. This includes various types of dementia, Alzheimer's, and other cognitive disorders.
In addition to assessing cancer, a PET scan can assist in determining the extent and nature of infections. By visualizing the areas of inflammation and infection, doctors can better understand the spread of the infection and tailor treatment strategies accordingly. This is especially important in cases where the cause of infection is unclear from other diagnostic tools.
PET scans can also be utilized to evaluate certain neurological conditions. By identifying regions of abnormal metabolic activity in the brain, doctors can assess the extent and nature of the damage or disease process. This information can be crucial in planning treatment strategies and monitoring the progression of the condition. This helps in better understanding the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
A growth mindset is a belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. It's not about innate talent, but about the power of effort, persistence, and learning from setbacks. Individuals with a growth mindset embrace challenges as opportunities to learn and grow, viewing mistakes as valuable feedback rather than indicators of fixed limitations. This fundamental shift in perspective is crucial for personal and professional development, fostering resilience and a proactive approach to learning.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques in Pet Urinalysis
Microscopic Examination: Unveiling Cellular Clues
Microscopic examination of a urine sample is crucial for identifying abnormalities beyond what a dipstick test can reveal. This technique allows veterinary professionals to observe various cellular components like red blood cells, white blood cells, and epithelial cells. The presence and morphology of these cells can provide insights into underlying conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease, or even certain types of cancers. Careful observation of cell sizes, shapes, and the presence of abnormal crystals or casts further refines the diagnostic picture, assisting in pinpointing the specific cause of the issue and guiding targeted treatment.
Proteinuria: A Window into Kidney Health
Elevated protein levels in urine, known as proteinuria, can be a significant indicator of kidney disease. While some protein is normally present in urine, excessive amounts can suggest damage to the delicate filtering structures within the kidneys. Understanding the specific types and amounts of protein present helps differentiate between various kidney conditions and guide treatment strategies. This analysis is crucial for monitoring the progression of kidney disease and assessing the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
Specific Gravity and Osmolality: Evaluating Hydration Status
Analyzing specific gravity and osmolality provides valuable information about a pet's hydration status and kidney function. Specific gravity reflects the concentration of dissolved substances in the urine, while osmolality measures the total number of dissolved particles. Variations from the expected range can point to dehydration, overhydration, diabetes insipidus, or other conditions that impact fluid balance. These measurements are essential for guiding fluid therapy and ensuring appropriate treatment for animals experiencing hydration imbalances.
Urocrystals: A Diagnostic Puzzle
The presence of crystals in urine, known as urocrystals, can be a key diagnostic indicator for various conditions. Different types of crystals form under specific circumstances, and their identification can help pinpoint the underlying cause. For example, calcium oxalate crystals might suggest a dietary issue, while struvite crystals could indicate a urinary tract infection. Analyzing the shape, size, and composition of these crystals is essential for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment approaches.
Culture and Sensitivity Testing: Identifying Pathogens
In cases of suspected urinary tract infections (UTIs), culture and sensitivity testing is crucial for identifying the specific bacteria responsible. This process isolates bacteria from the urine sample and tests their susceptibility to various antibiotics. The results guide veterinarians in selecting the most effective antibiotic treatment, minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance and ensuring prompt resolution of the infection. This targeted approach is vital for optimizing patient recovery and preventing potential complications.
Advanced Imaging Techniques: Visualizing the Urinary Tract
While urinalysis is a fundamental diagnostic tool, advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound, X-rays, and CT scans can provide detailed visual information about the urinary tract. These non-invasive procedures allow veterinarians to visualize the kidneys, bladder, and other structures, enabling identification of anatomical abnormalities, stones, tumors, or blockages. The combination of urinalysis with imaging provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and managing urinary system disorders in animals.
Read more about Urinalysis for Pets: What It Can Tell You
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet