Understanding Pet Medications: What You Need to Know
Oral medications are often the most common route for administering pet medications. These include tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions. Tablets and capsules typically contain a precise dosage of the active ingredient, which needs to be administered with care and accuracy, considering the size of the pet. Liquid medications can be easier to administer for some pets, but accurate measurement is critical to ensure the correct dosage.
Proper handling and administration techniques vary depending on the type of oral medication. For example, some tablets need to be crushed or dissolved before administration, while others should be given whole. Incorrect administration can lead to ineffective treatment or potential harm. Consult your veterinarian for precise instructions on administering oral medications to your pet.
Topical Medications: Ointments, Creams, and Sprays
Topical medications are applied directly to the affected area of the pet's skin or coat. These include ointments, creams, and sprays. These medications are often used to treat skin conditions, parasites, or localized infections. Understanding the specific instructions for application is vital to ensure effective treatment and avoid potential irritation or adverse reactions.
The application technique for topical medications can vary considerably. Some ointments are applied directly to the affected area, while others may require mixing with a carrier solution. It's important to follow the veterinarian's instructions precisely, including the frequency and duration of application, to achieve the desired outcome.
Injectable Medications: Subcutaneous, Intramuscular, and Intravenous
Injectable medications are administered directly into the pet's body using a needle and syringe. These medications are typically used for conditions requiring rapid or sustained therapeutic effects. Different types of injections, such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous, are used depending on the medication and the pet's health needs. The veterinarian will determine the most appropriate injection method.
Injectable medications require specialized knowledge and skill for proper administration. Only trained and qualified veterinary professionals should administer injections. Improper technique or dosage can lead to complications, including discomfort, infection, or even potentially life-threatening consequences.
Nutritional Supplements and Dietary Changes
Many pets benefit from nutritional supplements or dietary changes to support their overall health and well-being. These supplements can be in the form of powders, tablets, or added to their food. They can be crucial for maintaining a healthy weight, supporting immune function, or addressing specific dietary requirements.
Dietary changes, like incorporating specific foods, can significantly impact a pet's health. Consulting with a veterinarian is essential to determine the most appropriate nutritional plan for your pet's needs. Dietary changes should be implemented gradually to minimize potential digestive upset. Your veterinarian can provide tailored advice on the best nutritional support for your pet's unique requirements.
Parasite Medications: Preventative and Treatment
Parasite medications are essential for preventing and treating internal and external parasites in pets. These medications come in various forms, including oral tablets, topical solutions, and even flea collars. Choosing the right medication for your pet's specific needs is crucial for preventing the spread of diseases and maintaining their overall health.
Understanding Dosage and Administration Schedules
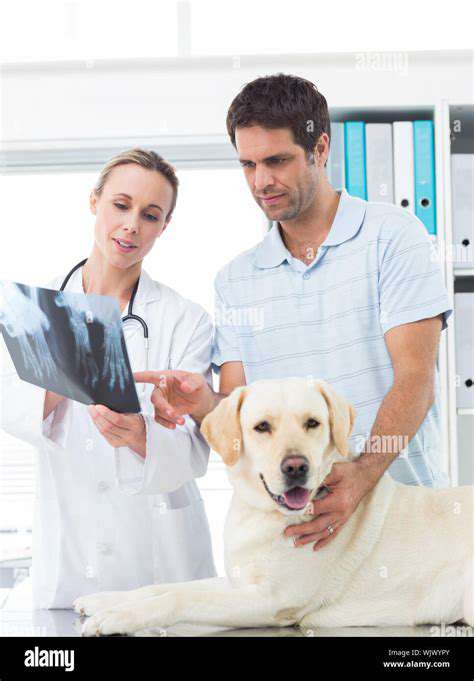
Accurate dosage and adherence to the prescribed administration schedule are critical for the effectiveness and safety of pet medications. Following the veterinarian's instructions meticulously is essential. Overdosing or underdosing can lead to adverse effects. Always consult your veterinarian with any questions or concerns about your pet's medication regime.
Dosage and Administration: Key Considerations
Understanding Dosage Regimens
Dosage and administration are critical aspects of medication management, directly impacting treatment efficacy and minimizing adverse effects. Understanding the prescribed dosage regimen, including frequency, route, and duration, is paramount for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes. Proper adherence to the prescribed dosage regimen is essential for successful treatment and preventing complications. A clear understanding of the dosage and administration instructions is vital to ensure the medication is taken correctly and effectively.
Different medications have different recommended dosages based on factors such as the patient's age, weight, medical history, and the specific condition being treated. It is crucial to carefully follow the instructions provided by a healthcare professional, as deviations can lead to unpredictable or harmful consequences. Always consult with a doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions about the dosage or administration of your medication.
Route of Administration
The route of administration significantly influences how a medication is absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Oral administration, for example, involves taking the medication by mouth, allowing for gradual absorption into the bloodstream. Other routes, such as intravenous or intramuscular injections, deliver medications directly into the bloodstream or muscle tissue, leading to faster absorption and potentially greater efficacy for certain conditions.
Parenteral routes, including intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections, bypass the digestive system, providing rapid drug delivery. This is often crucial in emergency situations or when rapid therapeutic action is necessary. Different routes also impact the potential for side effects, and healthcare professionals carefully consider the route to minimize these risks.
Important Considerations for Administration
Proper storage conditions for medications are critical to maintaining their potency and effectiveness. Storing medications in appropriate environments, such as a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight, prevents degradation and ensures the medication's efficacy. Failing to adhere to proper storage guidelines can diminish the medication's potency, rendering it less effective or potentially harmful.
Timing of administration can also play a crucial role in maximizing the effectiveness of a medication. Some medications are best taken with food to enhance absorption, while others should be taken on an empty stomach. Adhering to the recommended timing is essential for optimal therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential side effects.
Patient Education and Adherence
Patient education plays a vital role in ensuring that patients understand and follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions. Clear and concise instructions, along with readily available resources, empower patients to effectively manage their medications. Educating patients on the importance of adherence to the prescribed regimen is crucial for successful treatment.
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor medication effectiveness and address any concerns or side effects. Open communication between patients and healthcare professionals facilitates prompt adjustments to the dosage regimen as needed, ensuring optimal therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential harm. Proper patient education also empowers them to actively participate in their health management.