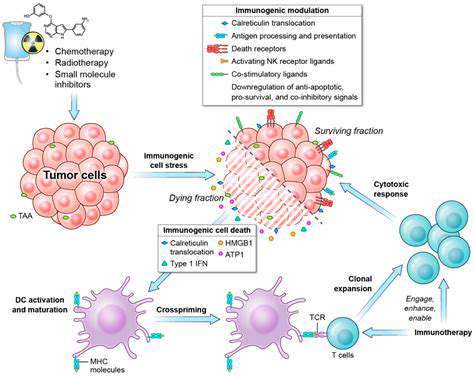
Understanding Pet Food Miles: Local vs Imported Ingredients
Nutritional Considerations: Are Local Ingredients Always Better?

Nutritional Considerations for Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance affects digestion for many people worldwide. This condition stems from insufficient lactase enzyme production, which breaks down lactose in dairy. Without proper management, this can lead to uncomfortable digestive symptoms and nutritional gaps. Many processed foods contain hidden lactose, including some sauces and medications, making label reading essential.
Dairy Alternatives Worth Exploring
The market now offers diverse plant-based milk options - almond, soy, oat, and rice varieties - often enriched with calcium and vitamin D. These alternatives not only match dairy's nutritional profile but also introduce exciting flavors and textures to meals. From morning cereals to baked goods, they seamlessly substitute dairy in most recipes while maintaining taste and nutrition.
Maintaining Bone Health Without Dairy
While dairy provides calcium and vitamin D, lactose-intolerant individuals can obtain these nutrients from leafy greens, fortified foods, tofu, and certain fish. Vitamin D supplements become particularly important during winter months when sunlight exposure decreases. Regular intake of these alternatives helps maintain strong bones and overall health.
Health Implications of Unmanaged Intolerance
Ignoring lactose intolerance can lead to ongoing digestive discomfort and potential nutrient deficiencies. Proactive dietary management prevents these issues and supports long-term wellness. A well-planned diet ensures the body receives all necessary nutrients despite dairy limitations.
Avoiding Nutritional Shortfalls
Dairy elimination without proper substitution may create gaps in calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients. Strategic meal planning and professional nutritional guidance help maintain balanced nutrient intake. Registered dietitians can create personalized plans addressing individual needs and preferences.
Crafting a Balanced Lactose-Free Diet
Effective lactose intolerance management combines diverse food groups - fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. This approach, complemented by lactose-free alternatives, supports digestive comfort and overall health. Careful food selection and preparation ensure meals remain nutritious and enjoyable.
Transparency and Choosing the Right Pet Food
The Essentials of Pet Food Transparency
Informed pet ownership begins with understanding food ingredients and origins. Clear labeling reveals processing methods and ingredient sources, allowing owners to avoid harmful additives. Some manufacturers now provide detailed sourcing information, though consumers must actively research to make optimal choices.
Why Ingredient Origins Matter
Ingredient sourcing directly affects food quality, nutrition, and environmental impact. Locally-sourced ingredients often offer superior freshness and smaller ecological footprints. Sustainable farming practices further enhance nutritional value while reducing environmental harm.
Comparing Local and Global Production
Local pet food production minimizes transportation, reducing carbon emissions and preserving ingredient quality. In contrast, globally-sourced products accumulate greater environmental costs through extended supply chains, potentially compromising freshness.
Environmental Costs of Pet Food Transport
Long-distance ingredient shipping significantly increases greenhouse gas emissions. The pet food industry's carbon footprint grows with every mile ingredients travel between farms, processors, and consumers. Environmentally-conscious owners should consider transportation impacts when selecting products.
Nutritional Differences in Ingredient Sources
Locally-sourced ingredients typically retain more nutrients due to reduced transit times. Processing methods also affect nutrient bioavailability - some techniques preserve nutrition better than others. These factors collectively determine a food's health benefits for pets.
Deciphering Pet Food Labels
Label terminology like natural or grain-free requires careful interpretation. Comparing labels across brands reveals significant differences in nutritional content and sourcing practices. Understanding these details helps owners select optimal foods for their pets' specific needs.
Personalized Pet Nutrition
Choosing appropriate pet food involves considering age, breed, activity level, and any allergies. Transparent labeling enables owners to match products to their pet's unique requirements. A nutritionally-balanced, thoughtfully-sourced diet contributes significantly to a pet's health and longevity.
Read more about Understanding Pet Food Miles: Local vs Imported Ingredients
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet