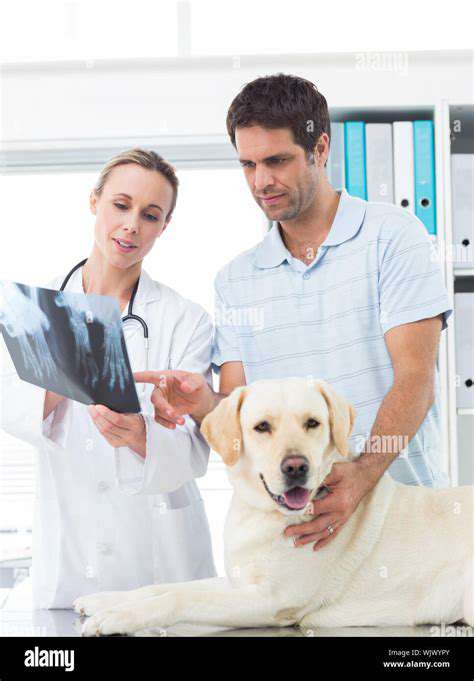
Recognizing the Signs of Pet Illness: Early Detection Saves Lives
Recognizing Changes in Appetite and Thirst
Understanding the Significance of Appetite Changes
Changes in appetite, whether an increase or decrease, can be a significant indicator of underlying health issues. Appetite is a complex physiological process influenced by numerous factors, including hormonal fluctuations, stress levels, and even the types of foods consumed. Recognizing these changes and understanding their potential causes can be crucial for maintaining overall well-being and preventing more serious health complications.
It's important to pay attention to these shifts, as they can serve as early warning signs for conditions ranging from mild nutrient deficiencies to more serious medical concerns. Early detection and intervention can often lead to better outcomes and more effective management of any underlying issues.
Identifying Potential Medical Causes
Numerous medical conditions can affect appetite. These can range from relatively common issues like pregnancy and thyroid problems to more serious conditions like cancer and certain types of infections. Understanding the potential medical causes of appetite changes is essential for seeking appropriate medical advice.
Gastrointestinal issues, such as ulcers or inflammatory bowel disease, can also significantly impact appetite. Furthermore, certain medications can sometimes cause changes in appetite as a side effect.
The Role of Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can significantly impact appetite. Pregnancy, menstruation, menopause, and even the use of birth control pills can all influence feelings of hunger and fullness.
These hormonal shifts can lead to both increased and decreased appetite, and understanding these patterns is crucial for women to monitor their own health.
Psychological Factors Contributing to Appetite Changes
Stress, anxiety, and depression are all psychological factors that can significantly impact appetite. Periods of intense stress can lead to decreased appetite, while other psychological conditions might result in increased cravings and overeating.
Emotional eating, a common coping mechanism, can lead to unhealthy eating patterns and further exacerbate the issue. Understanding these psychological factors is crucial for managing appetite changes effectively.
Dietary and Lifestyle Factors
Dietary changes, such as introducing new foods or altering portion sizes, can impact appetite. The types of foods consumed, including the presence of certain ingredients or food intolerances, can also influence appetite levels.
Lifestyle factors, such as sleep deprivation, lack of exercise, and excessive caffeine consumption, can also play a role in appetite regulation. Addressing these lifestyle habits can often help to normalize appetite.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Impact
Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in vitamins and minerals, can impact appetite. A lack of essential nutrients can lead to fatigue, weakness, and changes in hunger signals.
Identifying potential deficiencies through a balanced diet and regular checkups can help to address these issues effectively. Consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized advice.
Seeking Professional Medical Attention
Persistent or unexplained changes in appetite should always prompt a visit to a healthcare professional. Ignoring these changes could potentially mask underlying health conditions and delay necessary treatment.
A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough evaluation, consider your medical history, and provide appropriate recommendations to address the specific cause of your appetite changes. Don't hesitate to reach out for help if you're experiencing persistent changes in your appetite.

Read more about Recognizing the Signs of Pet Illness: Early Detection Saves Lives
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet