Parvovirus in Puppies: Prevention and Treatment

Vaccination Protocols
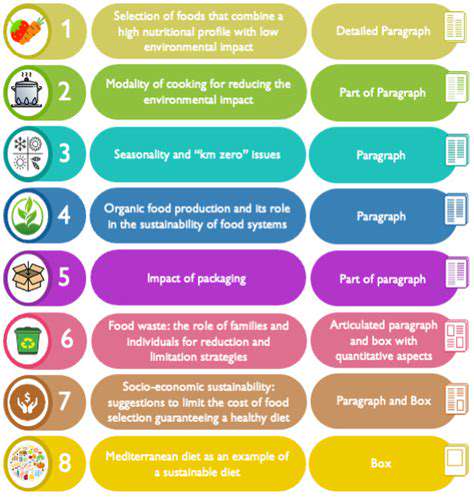
Vaccination is the cornerstone of parvovirus prevention. A series of carefully administered vaccines, typically starting at six to eight weeks of age, are crucial for building immunity. These vaccines provide a strong defense against the virus, significantly reducing the risk of infection. It's essential to adhere strictly to the veterinarian's recommended vaccination schedule to ensure optimal protection for your puppy.
Puppies require multiple doses of the vaccine to develop a robust immune response. Missing or delaying these vaccinations can leave your puppy vulnerable to the virus, highlighting the importance of proactive veterinary care.
Environmental Sanitation
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment is vital in preventing parvovirus transmission. Parvovirus can survive for extended periods in the environment, clinging to surfaces and objects, and poses a significant risk if not properly addressed. Prompt and thorough cleaning of areas where your puppy spends time is essential.
This includes disinfecting areas like kennels, playpens, and even the floors of your home. Using a specialized parvovirus disinfectant is recommended to effectively eliminate the virus from surfaces.
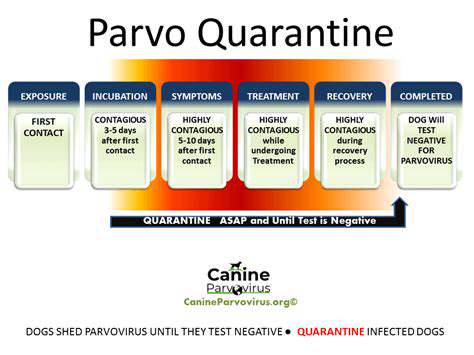
Quarantine Procedures
When introducing a new puppy to your home, or if your puppy comes into contact with other animals from outside your home, a quarantine period is highly recommended. This period allows you to monitor the puppy for any signs of illness and prevents the potential spread of parvovirus to your existing pets. Quarantine periods should be followed strictly to help prevent the spread of the virus.
During this period, the new puppy should be kept separate from other pets, and all contact should be limited. This precaution is critical in preventing the transmission of parvovirus within your household.
Dietary Considerations
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a vital role in supporting your puppy's overall health and immune system, which is crucial for combating parvovirus. Providing a diet formulated for growing puppies, with sufficient protein and essential nutrients, strengthens their immune response, making them better equipped to fight off infections. Nutritional deficiencies can weaken a puppy's ability to resist illness, so a good diet is essential.
Early Detection and Veterinary Care
Early detection of parvovirus symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Recognizing signs like vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, and loss of appetite promptly is essential. Any indication of illness should prompt immediate veterinary consultation. Veterinary intervention is critical in managing the condition and ensuring a positive outcome.
Prompt veterinary care is often essential for saving the life of an affected puppy. Treatment options can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but early intervention significantly increases the chances of successful recovery.
Over-tourism places immense strain on local communities. Businesses struggle to accommodate the influx of visitors, often leading to inflated prices and a decline in the quality of life for residents. This can manifest in overcrowded streets, inadequate infrastructure, and a loss of local character as businesses cater primarily to tourists, neglecting the needs of local patrons. The increased demand for resources, such as water and energy, also negatively impacts the environment and the well-being of the community.
Long-Term Outlook and Recovery from Parvovirus
Long-Term Recovery Potential
The long-term outlook for recovery hinges on several key factors, including the effectiveness of ongoing interventions and the resilience of affected communities. A crucial aspect of long-term recovery is the development of sustainable infrastructure that can withstand future shocks, whether environmental or societal. This encompasses not only physical rebuilding, but also the establishment of robust systems for disaster preparedness and response. The ability of individuals and communities to adapt to changing circumstances and rebuild their livelihoods is equally important.
Furthermore, fostering economic growth and job creation is essential for sustained recovery. Investments in education and vocational training programs can equip individuals with the skills needed to participate in the evolving job market, and this will be a key element in creating a thriving and resilient future. Initiatives focused on micro-enterprise development and small business support can also be instrumental in creating a sustainable economic foundation for the region.
Addressing Underlying Causes of Vulnerability
A thorough assessment of the factors that contributed to the initial crisis is vital for preventing future occurrences. A crucial component of this assessment is identifying and addressing the underlying causes of vulnerability, such as inadequate infrastructure, environmental degradation, and social inequalities. Understanding these vulnerabilities is critical to implementing effective preventative measures and building resilience against future challenges.
Addressing these issues requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses governmental policies, community participation, and international cooperation. For example, investments in early warning systems, climate adaptation strategies, and social safety nets can significantly reduce vulnerability to future shocks. This proactive approach will ultimately lead to a more resilient and sustainable future.
Community-Based Approaches to Recovery
Community-based initiatives play a vital role in fostering long-term recovery and resilience. These initiatives should prioritize the empowerment of local communities, allowing them to actively participate in the planning and implementation of recovery strategies. This bottom-up approach recognizes the unique needs and perspectives of local residents and ensures that recovery efforts are tailored to the specific context of the affected region.
Engaging local communities in the decision-making process fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, which is crucial for long-term sustainability. This approach ensures that recovery efforts are not imposed from the outside, but rather are driven by the needs and priorities of the affected communities themselves, leading to more effective and meaningful outcomes. Local knowledge and expertise are invaluable assets in the recovery process.
Read more about Parvovirus in Puppies: Prevention and Treatment
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet