Grain Free vs Grain Inclusive Pet Food: The Debate

Grains: A Staple in Many Pet Diets
Grains are a common ingredient in pet food, often used as a source of energy and fiber. They provide readily available carbohydrates that fuel a pet's daily activities. Many commercially available pet foods rely on grains like rice, corn, and wheat to bulk up the food and keep the cost down. This makes them a practical and relatively inexpensive option for pet owners. However, the specific types of grains used and their processing methods can significantly impact the nutritional value and digestibility of the food.
Different grains offer varying nutritional profiles. For example, brown rice is often favored over white rice because of its higher fiber content, which can aid in digestive health. Similarly, oats can contribute to a pet's overall health and well-being due to their soluble fiber content. It's important to understand that the presence of grains in a pet food doesn't automatically equate to a healthy diet. The quality of the grain and the overall nutritional composition of the food are crucial factors to consider.
Potential Benefits of Grains in Pet Food
Grains can be a valuable source of energy for pets, particularly for active animals. The readily available carbohydrates in grains fuel their play, exercise, and overall daily activities. This energy source is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and supporting physical activity. Moreover, some grains contain essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to a pet's overall health and well-being.
The fiber content in certain grains can promote healthy digestion and regularity. This is particularly important for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption and immune function. Furthermore, the presence of specific vitamins and minerals in grains can support various bodily functions, contributing to a pet's overall well-being and longevity.
Digestibility and Potential Issues
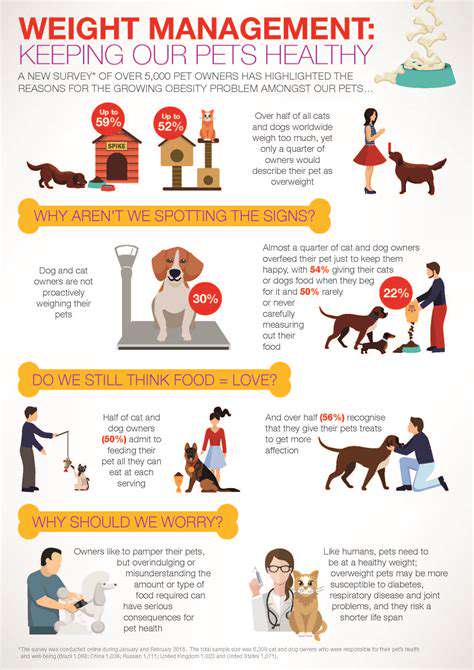
While grains can be a valuable source of nutrients, some pets may have difficulty digesting certain types of grains. This can lead to digestive issues such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea. The processing methods used for grains can also impact their digestibility. For instance, highly processed grains may be harder to digest than whole grains.
The specific grain type can also be a factor in digestive issues. Some grains are more allergenic than others. Certain dogs and cats may have sensitivities or allergies to grains, which can manifest as skin problems, itching, or digestive upset. Careful consideration of the pet's individual needs and sensitivities is crucial when selecting a grain-based pet food.
Alternative Ingredients and Considerations
There are alternative ingredients that can provide similar nutritional benefits to grains, such as potatoes, sweet potatoes, and legumes. These options can be a valuable alternative for pets with grain sensitivities or allergies. While grains are a common component in many pet food formulas, the potential for allergies and digestive issues necessitates a careful examination of the pet's individual needs.
Ultimately, the best approach is to consult with a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate dietary choices for your pet. They can assess your pet's specific needs and sensitivities to recommend a diet that supports their overall health and well-being, regardless of the inclusion of grains.
The Importance of a Balanced Diet
Regardless of whether a pet food contains grains, a balanced diet is essential for maintaining optimal health. A comprehensive approach that considers all nutritional components, including protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals, is crucial for a pet's overall well-being. It's not just about the presence or absence of grains; the overall nutritional profile of the food plays a significant role in supporting your pet's health.
Furthermore, dietary needs vary based on factors like age, breed, and activity level. A veterinarian can provide personalized recommendations tailored to your pet's unique requirements. This ensures that your pet receives the specific nutrients they need to thrive.
Potential Pitfalls of Grain-Free Diets
Potential Digestive Issues
One of the most significant concerns with grain-free diets for pets is the potential for digestive upset. Many grain-free pet foods rely heavily on alternative ingredients, such as legumes, potatoes, and other starches, which can sometimes be poorly digested or cause inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to symptoms like diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort. Owners may notice a change in stool consistency or frequency, which can be quite alarming and require veterinary intervention to rule out other potential causes. It's crucial to monitor your pet closely for any digestive changes, and consult with your veterinarian if you suspect a problem.
Furthermore, the rapid shift in dietary components from a grain-inclusive diet to a grain-free one can sometimes trigger an acute inflammatory response in the digestive system. This is especially true if the grain-free food contains ingredients that are highly allergenic or are poorly tolerated by the individual pet. This sudden shift can cause various digestive issues, from mild discomfort to more severe conditions, highlighting the importance of a gradual transition when changing a pet's diet.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Health Risks
While grain-free diets are often marketed as a healthier alternative, they can sometimes fall short in providing a complete and balanced nutritional profile. Some grain-free pet foods, particularly those relying on limited ingredients or those not formulated with careful attention to nutrient density, may lack essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients crucial for optimal health. This nutritional imbalance can lead to a variety of health problems, ranging from mild deficiencies to more serious conditions, depending on the specific nutrients lacking and the duration of the deficiency. This is a critical consideration for pet owners, as it is essential to ensure that the grain-free diet meets the specific nutritional needs of their pet.
Another potential concern is the link between certain grain-free diets and heart conditions, specifically dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). While the exact cause-and-effect relationship is still being investigated, some studies suggest a correlation between the consumption of certain grain-free ingredients and an increased risk of DCM, particularly in certain breeds. This underscores the importance of consulting with your veterinarian and carefully evaluating the ingredients and nutritional content of any grain-free food you consider for your pet.
The potential long-term health consequences of a poorly formulated grain-free diet are significant. Chronic deficiencies in essential nutrients can lead to organ damage, weakened immune systems, and other health problems that may not be immediately apparent. This highlights the importance of choosing a grain-free diet that is formulated by a reputable manufacturer and is carefully monitored for its nutritional value, ensuring it's suitable for your pet's breed and overall health.
The potential for adverse reactions, from mild digestive upset to serious health issues, emphasizes the need for careful consideration when choosing a grain-free diet for your pet. Thorough research, consultation with your veterinarian, and careful monitoring are essential to minimize risks and ensure the well-being of your furry friend.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming various sectors, and mental health is no exception. AI-powered tools can offer quick and accessible mental health assessments, potentially identifying individuals at risk for various conditions. These assessments can provide preliminary data that can inform clinicians and support faster intervention for those in need. This can lead to more efficient and targeted interventions, especially in areas with limited mental health resources.

Read more about Grain Free vs Grain Inclusive Pet Food: The Debate
Hot Recommendations
- Holistic Pet Health: Integrating Approaches
- The Future of Pet Identification: Biometric Scanners
- Service Dogs for PTSD: A Guide to Support
- The Benefits of Non Anesthetic Professional Teeth Cleaning
- Herbal Supplements for Pet Joint Health
- The Intersection of IoT and Pet Wellness
- Healthy Weight Management for Senior Pets
- The Best Pet Beds for Orthopedic Support and Comfort
- Competitive Dog Sports: Agility, Flyball, Dock Diving
- Luxury Pet Hotels: Pampering Your Beloved Pet